A Multi-Objective Double Row Layout Problem Considering Safety Distances and Geometrical Constraints
Main Article Content
Keywords
double row layout problem, multi-objective optimization, variable neighborhood search, safety distance, geometric constraint
Abstract
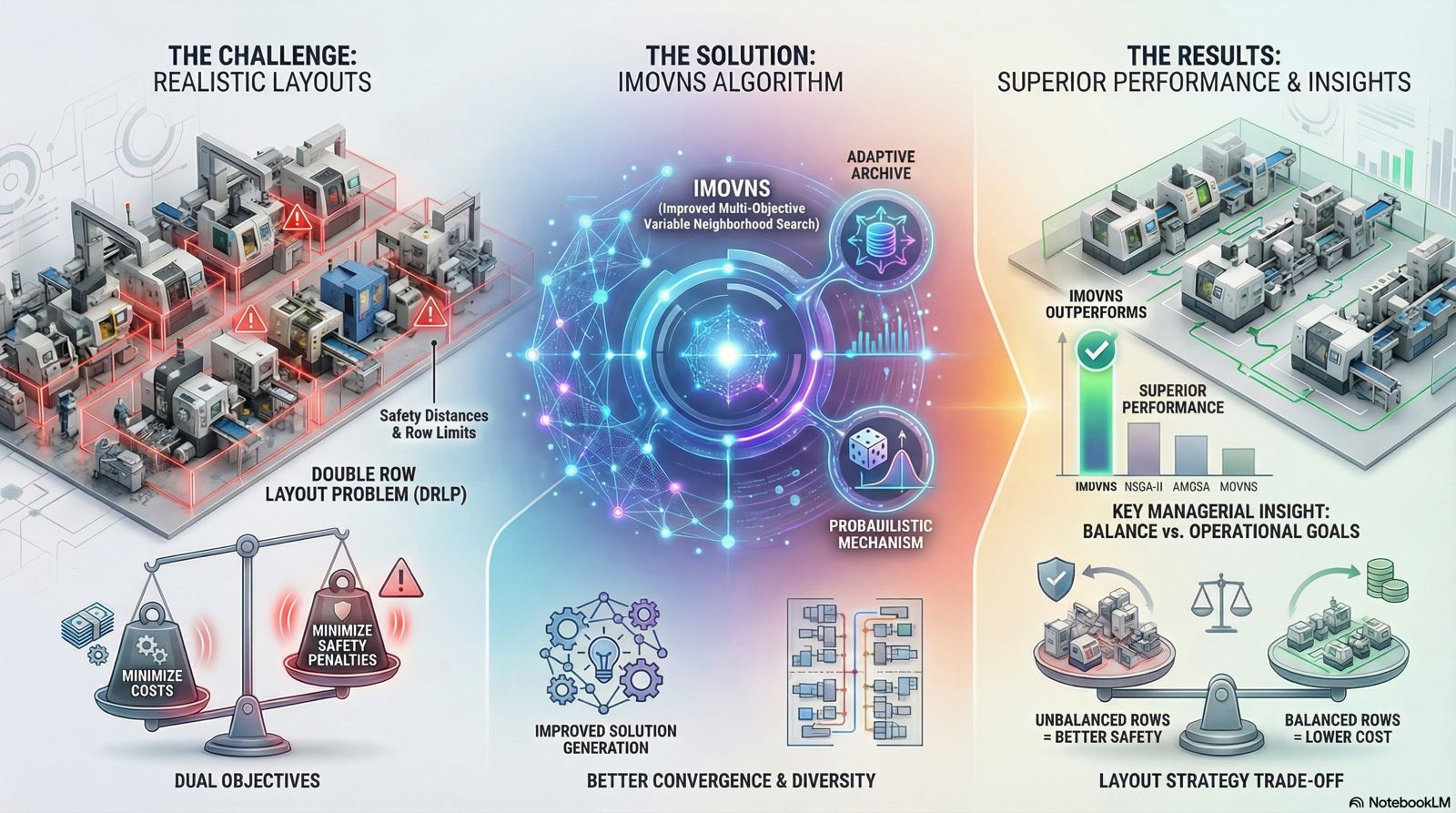
This study addresses an enhanced version of the Double Row Layout Problem (DRLP) by incorporating two critical constraints: minimum safety distances between machines and geometric limitations on row lengths. A bi-objective mixed-integer non-linear programming (MINLP) model is formulated to simultaneously minimize material handling costs and penalties for violating safety distance requirements. To solve the problem efficiently, a novel metaheuristic called Improved Multi-Objective Variable Neighborhood Search (IMOVNS) is proposed. IMOVNS extends the standard MOVNS by integrating an adaptive archive update strategy and a probabilistic acceptance mechanism inspired by AMOSA, thereby improving both convergence and diversity in Pareto front generation. This study contributes to the layout optimization literature by proposing a tailored MOVNS variant explicitly designed for safety-aware and geometry-constrained DRLP, a challenging problem variant that has received limited attention in prior research. Extensive experiments on 27 DRLP instances show that IMOVNS demonstrates strong performance, significantly outperforming NSGA-II and showing competitive or superior results compared to AMOSA and MOVNS in terms of convergence and solution diversity. Statistical tests further confirm the significant superiority of IMOVNS, particularly over NSGA-II. Additionally, a key managerial insight reveals that layouts with unbalanced row lengths favour safety compliance, while balanced layouts minimize material handling costs. The Pareto-optimal solutions generated by IMOVNS enable decision-makers to select layout configurations that align with specific operational priorities. These findings highlight the practical relevance and robustness of IMOVNS in solving real-world multi-objective facility layout problems under complex spatial and safety constraints.
Downloads
References
[2] A. Mohamadghasemi and A. Hadi-Vencheh, “An integrated synthetic value of fuzzy judgments and nonlinear programming methodology for ranking the facility layout patterns,” Comput. Ind. Eng., vol. 62, no. 1, pp. 342–348, Feb. 2012, doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2011.10.004.
[3] J. Liu, H. Zhang, K. He, and S. Jiang, “Multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm based on objective space division for the unequal-area facility layout problem,” Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 102, pp. 179–192, Jul. 2018, doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2018.02.035.
[4] B. Keller and U. Buscher, “Single row layout models,” Eur. J. Oper. Res., vol. 245, no. 3, pp. 629–644, Sep. 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2015.03.016.
[5] J. Chung and J. M. A. Tanchoco, “The double row layout problem,” Int. J. Prod. Res., vol. 48, no. 3, pp. 709–727, Feb. 2010, doi: 10.1080/00207540802192126.
[6] G. Aiello, G. La Scalia, and M. Enea, “A multi objective genetic algorithm for the facility layout problem based upon slicing structure encoding,” Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 39, no. 12, pp. 10352–10358, Sep. 2012, doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2012.01.125.
[7] S. Ingole and D. Singh, “Unequal-area, fixed-shape facility layout problems using the firefly algorithm,” Eng. Optim., vol. 49, no. 7, pp. 1097–1115, Jul. 2017, doi: 10.1080/0305215X.2016.1235327.
[8] Y. H. Lee and M. H. Lee, “A shape-based block layout approach to facility layout problems using hybrid genetic algorithm,” Comput. Ind. Eng., vol. 42, no. 2–4, pp. 237–248, Apr. 2002, doi: 10.1016/S0360-8352(02)00018-9.
[9] J. E. C. Arroyo, R. Dos Santos Ottoni, and A. De Paiva Oliveira, “Multi-objective Variable Neighborhood Search Algorithms for a Single Machine Scheduling Problem with Distinct due Windows,” Electron. Notes Theor. Comput. Sci., vol. 281, pp. 5–19, Dec. 2011, doi: 10.1016/j.entcs.2011.11.022.
[10] A. Duarte, J. J. Pantrigo, E. G. Pardo, and N. Mladenovic, “Multi-objective variable neighborhood search: an application to combinatorial optimization problems,” J. Glob. Optim., vol. 63, no. 3, pp. 515–536, Nov. 2015, doi: 10.1007/s10898-014-213-z.
[11] P. J. M. Van Laarhoven and E. H. L. Aarts, “Simulated annealing,” in Simulated Annealing: Theory and Applications, Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 1987, pp. 7–15. doi: 10.1007/978-94-015-7744-1_2.
[12] Z. Zhang and C. C. Murray, “A corrected formulation for the double row layout problem,” Int. J. Prod. Res., vol. 50, no. 15, pp. 4220–4223, Aug. 2012, doi: 10.1080/00207543.2011.603371.
[13] C. C. Murray, A. E. Smith, and Z. Zhang, “An efficient local search heuristic for the double row layout problem with asymmetric material flow,” Int. J. Prod. Res., vol. 51, no. 20, pp. 6129–6139, Oct. 2013, doi: 10.1080/00207543.2013.803168.
[14] A. R. S. Amaral, “A mixed-integer programming formulation for the double row layout of machines in manufacturing systems,” Int. J. Prod. Res., vol. 57, no. 1, pp. 34–47, Jan. 2019, doi: 10.1080/00207543.2018.1457811.
[15] A. Drira, H. Pierreval, and S. Hajri-Gabouj, “Facility layout problems: A survey,” Annu. Rev. Control, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 255–267, Jan. 2007, doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2007.04.001.
[16] S. P. Singh and R. R. K. Sharma, “A review of different approaches to the facility layout problems,” Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., vol. 30, no. 5–6, pp. 425–433, Sep. 2006, doi: 10.1007/s00170-005-0087-9.
[17] J. Chae and A. C. Regan, “A mixed integer programming model for a double row layout problem,” Comput. Ind. Eng., vol. 140, p. 106244, Feb. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2019.106244.
[18] S. Duan and L. Kang, “An Enhanced Multiobjective Double Row Layout Model considering the Machine Breakdowns,” Comput. Intell. Neurosci., vol. 2022, pp. 1–14, Aug. 2022, doi: 10.1155/2022/6289609.
[19] Z. Zhang, L. Wu, Z. Wu, W. Zhang, S. Jia, and T. Peng, “Energy-Saving Oriented Manufacturing Workshop Facility Layout: A Solution Approach Using Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization,” Sustainability, vol. 14, no. 5, p. 2788, Feb. 2022, doi: 10.3390/su14052788.
[20] M. Gülşen, C. C. Murray, and A. E. Smith, “Double-row facility layout with replicate machines and split flows,” Comput. Oper. Res., vol. 108, pp. 20–32, Aug. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2019.03.009.
[21] P. Pérez-Gosende, J. Mula, and M. Díaz-Madroñero, “Facility layout planning. An extended literature review,” Int. J. Prod. Res., vol. 59, no. 12, pp. 3777–3816, Jun. 2021, doi: 10.1080/00207543.2021.1897176.
[22] A. P. Rifai, S. T. Windras Mara, H. Ridho, and R. Norcahyo, “The double row layout problem with safety consideration: a two-stage variable neighborhood search approach,” J. Ind. Prod. Eng., vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 181–195, Apr. 2022, doi: 10.1080/21681015.2021.1968964.
[23] W. Isnaini, A. P. Rifai, N. M. E. Nurmasari, N. A. Masruroh, I. B. Dharma, and V. E. Andriani, “Sequential use of blocplan, solver, and particle swarm optimization (PSO) to optimize the double row facility layout,” Int. J. Prod. Manag. Eng., vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 117–124, May 2024, doi: 10.4995/ijpme.2024.20061.
[24] X. Zuo, C. C. Murray, and A. E. Smith, “Solving an Extended Double Row Layout Problem Using Multiobjective Tabu Search and Linear Programming,” IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng., vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 1122–1132, Oct. 2014, doi: 10.1109/TASE.2014.2304471.
[25] S. Wang, X. Zuo, X. Liu, X. Zhao, and J. Li, “Solving dynamic double row layout problem via combining simulated annealing and mathematical programming,” Appl. Soft Comput., vol. 37, pp. 303–310, Dec. 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2015.08.023.
[26] F. Jolai, R. Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, and M. Taghipour, “A multi-objective particle swarm optimisation algorithm for unequal sized dynamic facility layout problem with pickup/drop-off locations,” Int. J. Prod. Res., vol. 50, no. 15, pp. 4279–4293, Aug. 2012, doi: 10.1080/00207543.2011.613863.
[27] H. Rezazadeh, M. Ghazanfari, M. Saidi-Mehrabad, and S. Jafar Sadjadi, “An extended discrete particle swarm optimization algorithm for the dynamic facility layout problem,” J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. A, vol. 10, no. 4, pp.
520–529, Apr. 2009, doi: 10.1631/jzus.A0820284.
[28] A. Derakhshan Asl, K. Y. Wong, and M. K. Tiwari, “Unequal-area stochastic facility layout problems: solutions using improved covariance matrix adaptation evolution strategy, particle swarm optimisation, and genetic algorithm,” Int. J. Prod. Res., vol. 54, no. 3, pp. 799–823, Feb. 2016, doi: 10.1080/00207543.2015.1070217.
[29] S. RazaviAlavi and S. AbouRizk, “Genetic Algorithm–Simulation Framework for Decision Making in Construction Site Layout Planning,” J. Constr. Eng. Manag., vol. 143, no. 1, p. 04016084, Jan. 2017, doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0001213.
[30] N. Mladenović and P. Hansen, “Variable neighborhood search,” Comput. Oper. Res., vol. 24, no. 11, pp. 1097–1100, Nov. 1997, doi: 10.1016/S0305-0548(97)00031-2.
[31] D. Matić, J. Kratica, V. Filipović, and D. Dugošija, “Variable neighborhood search for Multiple Level Warehouse Layout Problem,” Electron. Notes Discrete Math., vol. 39, pp. 161–168, Dec. 2012, doi: 10.1016/j.endm.2012.10.022.
[32] K. S. N. Ripon, K. Glette, K. N. Khan, M. Hovin, and J. Torresen, “Adaptive variable neighborhood search for solving multi-objective facility layout problems with unequal area facilities,” Swarm Evol. Comput., vol. 8, pp. 1–12, Feb. 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2012.07.003.
[33] P. Hansen and N. Mladenović, “Variable Neighborhood Search,” in Search Methodologies, E. K. Burke and G. Kendall, Eds., Boston, MA: Springer US, 2005, pp. 211–238. doi: 10.1007/0-387-28356-0_8.
[34] B. Jarboui, H. Derbel, S. Hanafi, and N. Mladenović, “Variable neighborhood search for location routing,” Comput. Oper. Res., vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 47–57, Jan. 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2012.05.009.
[35] S. Bandyopadhyay, S. Saha, U. Maulik, and K. Deb, “A Simulated Annealing-Based Multiobjective Optimization Algorithm: AMOSA,” IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput., vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 269–283, Jun. 2008, doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2007.900837.
[36] L. F. Muller, S. Spoorendonk, and D. Pisinger, “A hybrid adaptive large neighborhood search heuristic for lot- sizing with setup times,” Eur. J. Oper. Res., vol. 218, no. 3, pp. 614–623, May 2012, doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2011.11.036.
[37] D. Freitas, L. G. Lopes, and F. Morgado-Dias, “Particle Swarm Optimisation: A Historical Review Up to the Current Developments,” Entropy, vol. 22, no. 3, p. 362, Mar. 2020, doi: 10.3390/e22030362.
[38] D. M. Simmons, “One-Dimensional Space Allocation: An Ordering Algorithm,” Oper. Res., vol. 17, no. 5, pp. 812–826, Oct. 1969, doi: 10.1287/opre.17.5.812.
[39] A. R. S. Amaral, “On the exact solution of a facility layout problem,” Eur. J. Oper. Res., vol. 173, no. 2, pp. 508–518, Sep. 2006, doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2004.12.021.
[40] A. R. S. Amaral, “An Exact Approach to the One-Dimensional Facility Layout Problem,” Oper. Res., vol. 56, no. 4, pp. 1026–1033, Aug. 2008, doi: 10.1287/opre.1080.0548.
[41] A. R. S. Amaral, “A new lower bound for the single row facility layout problem,” Discrete Appl. Math., vol. 157, no. 1, pp. 183–190, Jan. 2009, doi: 10.1016/j.dam.2008.06.002.
[42] L. D. Secchin and A. R. S. Amaral, “An improved mixed-integer programming model for the double row layout of facilities,” Optim. Lett., vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 193–199, Feb. 2019, doi: 10.1007/s11590-018-1263-9.
[43] M. Laszczyk and P. B. Myszkowski, “Survey of quality measures for multi-objective optimization: Construction of complementary set of multi-objective quality measures,” Swarm Evol. Comput., vol. 48, pp. 109–133, Aug. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2019.04.001.
[44] M. Li and X. Yao, “Quality Evaluation of Solution Sets in Multiobjective Optimisation: A Survey,” ACM Comput. Surv., vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 1–38, Mar. 2020, doi: 10.1145/3300148.
[45] S. Rostami and F. Neri, “A fast hypervolume driven selection mechanism for many-objective optimisation problems,” Swarm Evol. Comput., vol. 34, pp. 50–67, Jun. 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2016.12.002.